What Is Nutrition?
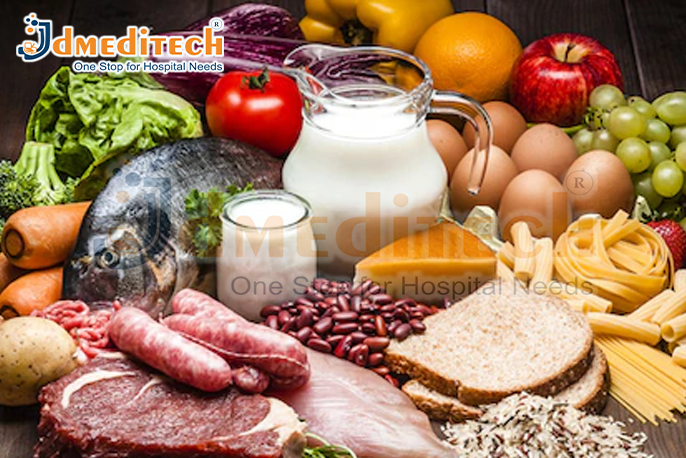
Nutrition is the science that studies how food and nutrients affect the growth, health, and functioning of the human body. Every bite of food we eat contains nutrients that provide energy, build and repair tissues, support immunity, and keep our organs working properly. Good nutrition helps prevent disease, improves overall well-being, and supports a healthy, active life.
Why Is Nutrition Important?
Your body needs a balanced supply of nutrients every day. These nutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, fiber, and water. Each nutrient has a specific role:
- Carbohydrates give energy.
- Proteins help build and repair tissues.
- Fats support brain health, hormone production, and energy storage.
- Vitamins and minerals regulate body functions and strengthen immunity.
- Fiber supports digestion.
- Water keeps every cell of your body hydrated and functioning.
When you eat a balanced diet, your body receives everything it needs to perform at its best. Poor nutrition, on the other hand, can lead to fatigue, weakened immunity, slow healing, and increased risk of lifestyle diseases like diabetes, obesity, and heart disease.
Nutrition as a Daily Practice
Good nutrition isn’t about strict diets—it’s about making healthier choices every day. Including whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats in your meals can have a powerful impact on long-term health. Staying hydrated, eating mindfully, and maintaining balanced portions are also key parts of good nutrition.
What Are Macronutrients?
Macronutrients are the nutrients your body needs in large amounts to function properly. They provide energy (calories) and support essential processes such as growth, metabolism, immunity, and overall health. The three main macronutrients are carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
-
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They break down into glucose, which fuels your brain, muscles, and organs.
Types of carbohydrates:
- Simple carbs: sugars found in fruits, milk, and processed foods
- Complex carbs: whole grains, vegetables, beans, lentils
Benefits:
- Provide quick and sustained energy
- Support brain function
- Help regulate digestion when taken as whole grains and fibre-rich foods
Healthy sources:
Whole wheat, brown rice, oats, millets, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
-
Proteins
Proteins are the building blocks of the body. They are essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues, muscles, hair, skin, and organs.
Why your body needs protein:
- Builds and repairs tissues
- Supports hormones and enzyme production
- Strengthens the immune system
Healthy sources:
Eggs, fish, chicken, dairy, paneer, lentils, beans, chickpeas, soy products, nuts and seeds.
-
Fats
Fats are a concentrated source of energy and play a vital role in brain health, cell structure, and hormone regulation.
Types of fats:
- Healthy fats: unsaturated fats (olive oil, nuts, seeds, avocados, fatty fish)
- Unhealthy fats: trans fats and excess saturated fats (fried foods, processed snacks)
Benefits of healthy fats:
- Enhance brain function
- Improve vitamin absorption (A, D, E, K)
- Support heart and hormonal health
Why Macronutrients Matter
A balanced intake of macronutrients ensures your body gets the right fuel to function efficiently. The exact ratio depends on age, lifestyle, physical activity, and individual health goals, but a well-balanced plate typically includes:
- Complex carbs
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
What Are Minerals?

Minerals are essential micronutrients that your body needs in small amounts to perform vital functions. Even though they are required in tiny quantities, minerals play a major role in keeping your bones strong, maintaining heart health, supporting nerve function, and helping your body produce energy.
Your body cannot make minerals on its own—they must come from the foods you eat.
Types of Minerals
-
Macro Minerals (Major Minerals)
These are needed in larger amounts.
Key Macro Minerals & Their Functions:
- Calcium—Builds strong bones and teeth; supports muscle function and nerve transmission.
Sources: Milk, yogurt, paneer, leafy greens, almonds. - Phosphorus—Helps build bones and teeth; involved in energy production.
Sources: Dairy, meat, fish, beans, nuts. - Magnesium—Supports muscle and nerve function; helps maintain heart rhythm.
Sources: Nuts, seeds, whole grains, leafy greens. - Sodium—Helps maintain fluid balance and nerve function.
Sources: Table salt, pickles, processed foods (consume in moderation). - Potassium—Regulates heart function, muscle contractions, and fluid balance.
Sources: Bananas, oranges, potatoes, lentils. - Chloride—Works with sodium to maintain fluid balance and digestion.
Sources: Salt, seaweed, tomatoes. - Sulfur—essential for protein synthesis and detoxification.
Sources: Garlic, onions, eggs, legumes.
-
Trace Minerals (Micro Minerals)
These are needed in very small amounts, but they are still crucial for good health.
Key Trace Minerals & Their Functions:
- Iron—Helps form hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in the blood.
Sources: Spinach, beans, red meat, lentils. - Zinc—Supports immunity, wound healing, and enzyme activity.
Sources: Nuts, seeds, dairy, seafood. - Iodine—essential for thyroid hormone production.
Sources: Iodized salt, seafood. - Selenium—Acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage.
Sources: Nuts (especially Brazil nuts), fish, and eggs. - Copper—Helps in red blood cell formation and immune function.
Sources: Nuts, seeds, and whole grains. - Manganese – Aids metabolism and bone formation.
Sources: Whole grains, nuts, leafy vegetables. - Fluoride—strengthens teeth and prevents cavities.
Sources: Fluoridated water, tea, seafood.
Why Are Minerals Important?
Minerals help your body:
✔ Build strong bones and teeth
✔ Maintain a healthy heartbeat
✔ Support nerve and muscle function
✔ Produce energy
✔ Boost immunity
✔ Balance body fluids
✔ Support growth and repair
Conclusion
Good nutrition doesn’t have to be complicated. By embracing whole foods, balancing your meals, staying hydrated, eating mindfully and adopting sustainable habits, you can make significant improvements to your health and energy levels over time.