Organ Donation
Organ donation is one of the most selfless acts a person can perform. It has the power to save multiple lives, restore health, and give hope to families waiting for a second chance. With thousands of patients around the world suffering from end-stage organ failure, organ donation plays a crucial role in modern medical care.
What Is Organ Donation?
Organ donation is the process of giving an organ or tissue to someone who needs a transplant. These organs can come from a living donor or a deceased donor. Once transplanted, they help replace damaged or failing organs and significantly improve or save a patient’s life.
Which Organs Can Be Donated?
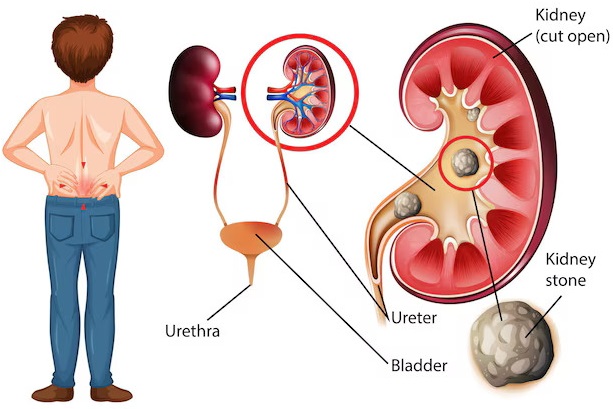
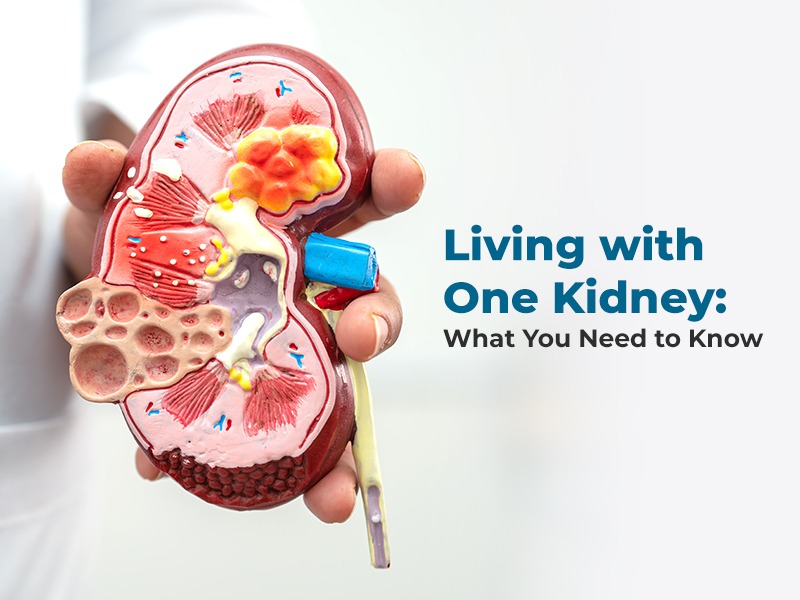
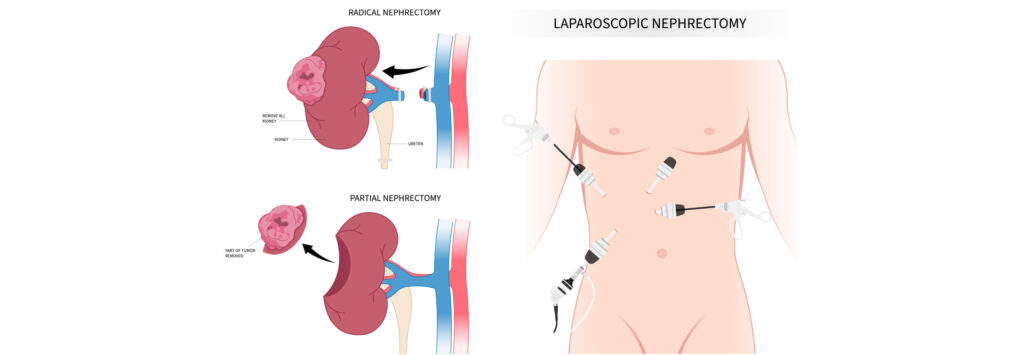
Kidneys
The only organ that can regrow
• The liver has a unique ability to regenerate.
• A portion of the liver can be donated by a living donor.
• The deceased liver can be split and used for two different recipients in some cases.
Liver
The only organ that can regrow
• The liver has a unique ability to regenerate.
• A portion of the liver can be donated by a living donor.
• The deceased liver can be split and used for two different recipients in some cases.
Heart
Life-saving for end-stage heart failure
• The heart can only be donated by a deceased donor.
• Heart transplant is required for patients with severe heart disease, cardiomyopathy, or congenital heart defects.
Lungs
• Lungs can be donated by a deceased donor.
• In some cases, two living donors can donate one lung lobe each.
Pancreas
• Can be donated by both living and deceased donors.
• Usually transplanted to treat type 1 diabetes or severe pancreatic failure.
Intestines
• Can be donated by a living donor (portion) or from a deceased donor.
• Transplant is rare but essential for patients with short bowel syndrome or severe intestinal disease.
Corneas (Eyes)
• One of the most common tissue donations.
• A single donor can restore sight for two people.
Skin
• Burn victims
• Plastic/reconstructive surgery
• Trauma cases
Heart Valves
Used to repair damaged heart valves caused by:
• Infection
• Congenital heart conditions
• Degenerative diseases
Bone and Tendons
• Orthopedic surgeries
• Joint reconstruction
• Spinal surgery
Veins & Arteries
• Bypass surgeries
• Vascular repair
Why Is Organ Donation Important?

Every year, the number of people waiting for transplants increases, but the number of donors does not keep up. Many patients lose their lives while waiting for a suitable organ match.
Organ donation is vital because it:
• Saves lives of patients with organ failure
• Improves quality of life
• Reduces long-term medical costs
• Helps families find purpose in loss
• Strengthens the healthcare system
Who Can Become an Organ Donor?
Almost anyone, regardless of age or medical history, can pledge to become a donor. Doctors will assess an individual’s medical condition at the time of death to determine which organs or tissues can be used.
Key donor eligibility factors:
• Overall health condition
• Cause of death
• Organ functionality
How Organ Donation Works
1. Registration or donor pledge by an individual
2. Medical evaluation after death
3. Consent from the family (if required)
4. Organ retrieval by transplant surgeons
5. Organ preservation and matching
6. Transplantation to a recipient in need
Organ Donation
Organ Donation in India
Organ Transplant
Organ Donation Process
Importance of Organ Donation
Types of Organ Donation
Conclusion
Organ donation is a noble act that has the power to transform lives. By choosing to become a donor, you help bridge the gap between organ shortage and demand. At JDMeditech, we are committed to supporting hospitals and healthcare professionals with advanced medical devices that aid successful organ retrieval and transplant procedures.