What is dilation and curettage (D&C)?
Dilation and curettage, sometimes known as D&C, is a gynecological procedure that involves the gentle opening of the cervix—the lower part of the uterus—and the removal of tissue from inside the uterus using a specialized instrument called a curette.
Depending on the circumstances, D&C can also be performed under suction—that is, vacuum—rather than sharp curettage.
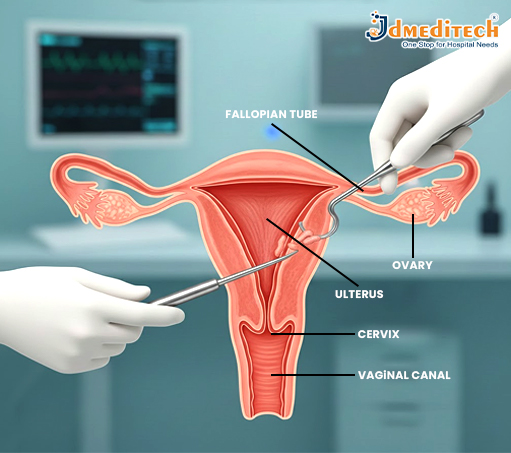
Why is D&C used?
D&C may be both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure. Indications for a D&C include:
• Investigating and diagnosing abnormal uterine bleeding, postmenopausal bleeding, and unexplained changes in menstrual cycles.
• Removing abnormal endometrial tissue, such as polyps, overgrown uterine lining, or suspected precancerous/cancerous changes.
• Clearing the uterus following a miscarriage or termination of pregnancy to ensure that no fetal or placental tissue remains.
• Removal of retained fragments of placenta after delivery or abortion, which may cause hemorrhage or infection.
Due to its flexibility and effectiveness, D&C remains one of the most common procedures when uterine sampling or tissue removal is required.
What to Expect—Procedure & Recovery Before the Procedure
•Your physician will discuss with you your medical history and advise any preoperative preparations, such as fasting or the use of any medication, as may be required.
• You will be asked to empty your bladder before the procedure. Depending on the indication and clinical circumstance, local or general anesthesia might be administered.
During the Procedure
• The speculum is inserted gently to visualize the cervix. Then, the cervix is slowly dilated using graduated dilators.
• Once dilation is sufficient, a metal or plastic curette or suction device is introduced to remove lining or tissue from the uterus.
• The tissue removed may be sent to the laboratory for analysis—looking for polyps, abnormal cells, or other pathology—if the D&C was performed for diagnostic purposes.
• The procedure itself is relatively quick; many D&Cs take about 10–20 minutes.
After the Procedure: Recovery & Home Care
•After D&C, many people experience mild cramping (like menstrual cramps) and light bleeding or spotting for a few days.
• Use sanitary pads, not tampons, to decrease your infection risk. Do not engage in vaginal intercourse, nor insert a tampon into the vagina, until your doctor lets you know that this will be safe, which is generally in about a week, though timing may vary.
• Most individuals return to normal activities within a few days.
•Many surgeons will schedule a follow-up appointment within 1–2 weeks, especially if the tissue was sent for pathology, to review the results and make sure the healing is normal.
Why Choose JD Meditech for Gynecology Instruments? ISO-certified manufacturer
• International-standard surgical instruments
• Rust-free, medical-grade stainless steel
• Ergonomic, surgeon-friendly design
• Export quality products with reliable performance
Our various products enjoy immense trust in hospitals, clinics, and healthcare facilities across the world.
Conclusion
D&C is a safe and effective diagnostic and treatment method for a variety of uterine problems. Availing themselves of the most advanced gynecology instruments offered by JD Meditech, healthcare professionals can conduct D&C with precision and confidence, ensuring better outcomes and patient care.
Get Connected:
+91 79909 93062 | +91 63513 72032 | exports@jdmeditech.com